Reduce Weld Preheat with Aeos™ ASTM A913

ASTM A992 structural steel is commonly used for construction projects, but there has recently been increased demand for the use of ASTM A913 quenched and self-tempered (QST) structural steel shapes as they offer metallurgical benefits including enhanced brittle fracture resistance, increased ductility and improved weldability.
Using a high-strength structural steel like Nucor’s Aeos™ ASTM A913 can offer significant benefits for design and construction teams looking to increase the efficiency of their projects including increased load-carrying capacities with higher yield strength (65, 70, 80 ksi), reduced embodied carbon intensity and improved fabrication and erection capabilities.
Preheat Requirements for ASTM A913
A913 is AWS D1.1-2020 prequalified which greatly reduces preheat requirements due to its carbon content and subsequent carbon equivalent values.
- Aeos Grades 50 and 65 are prequalified materials with a Category D classification, this reduces their minimum preheat requirements per American Welding Society (AWS) Structural Welding Code - D1.1, Table 5.8. This means Grades 50 and 65 do not require preheat for welding at various thicknesses if the sections meet a minimum base material temperature of 32 degrees Fahrenheit and the appropriate weld filler metal and welding processes are used.
- Aeos Grades 60, 65 and 70 are also prequalified materials with a Category C classification. The newest A913 Grade, Grade 80, is not prequalified material yet, but we expect Grade 80 to be added to the next edition of the AWS Structural Welding Code in 2025.
A reduction or elimination of welding preheat can have a significantly positive impact on a project’s schedule, as well as cost and energy consumption during the fabrication and erection process.
ASTM A913 Welding Guidelines
How do you best leverage Aeos’ fabrication and welding efficiencies for your next building construction project? In collaboration with Lincoln Electric, a global leader in arc welding, Nucor has developed the Aeos™ Welding Guidelines. Designed with fabricators, welders, engineers and construction professionals in mind, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of Aeos and can serve as your go-to reference for welding with A913 Grades 50, 65 and 70.
The Aeos Welding Guidelines contains an overview and three main sections*:
- Introduction — general overview of Aeos A913 metallurgical properties, the quench and self-tempering (QST) process, chemical and mechanical properties of A913 compared to A992 and sustainability benefits.
- Aeos Welding Considerations — approved welding procedures for fabrication shops and field welding, welding preheat and interpass temperatures, filler metal designations and commonly used electrodes based on Lincoln Electric’s product offerings and weld preheat savings when working with A913 versus A992.
- Aeos Fabrication FAQs — detailed guidance for fabrication shops with answers to frequently asked questions about heat straightening, stress relief, galvanizing, Charpy v-notch (CVN) testing, seismic applications and straight beam ultrasonic examination testing.
- Aeos A913 Availability — availability of the full range of wide flange structural steel sections available domestically from Nucor and a case study of a high-profile building in Chicago that utilized Aeos extensively in the design.
We hope this guide will provide valuable tips and tricks while also clarifying common misperceptions around welding with A913. Nucor is always looking for new ways to push the industry forward to meet the current and future needs of our partners and customers.
*Please note, these guidelines are not meant to serve as a replacement for professional judgment or calculations, nor to provide guidance on novel applications of A913 steel.
Nucor is your partner in finding solutions to your complex building and bridge construction projects. Contact our team of experts to learn more about Aeos, design assistance, construction market trends, overview of Nucor product offerings, sustainability studies and other steel construction solutions.
Benefits and Specificities of Welding with Aeos™
The quench and self-temper (QST) process used to create Aeos optimizes its grain structure to reduce weld preheat requirements and increase the efficiency of fabrication and erection. Because preheat conditions for welding Aeos can be greatly reduced or eliminated if welded in accordance with AWS D1.1 guidance, this can result in optimized fabrication and erection along with reduced energy consumption, both in the fabrication shop and on the jobsite. Removing preheat welding requirements can help move the material through the fabrication shop more quickly and save energy, as well as improve efficiency for erectors’ field welding operations. Additionally, energy consumption is reduced, further enhancing the environmental benefits of using Aeos.
The higher the strength of the steel you use, the less material you need to support the same loads. One of the benefits of using Aeos is its higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to A992 resulting in smaller member requirements and an overall reduction in steel tonnage for a project. As the tonnage and weld preheat requirements of structural members are reduced by using Aeos, several additional benefits can be realized, such as:
- Lower member cost
- Reduced global warming potential
- Efficient structural design
- Weld preheat savings
The grade of steel you use will help you determine which type of welding electrodes for your project. Electrodes are typically classified based on their tensile strength, so when using Aeos Grade 65 which has a tensile strength of 80 ksi, an E80XX electrode should be used in lieu of the typical E70XX that is used for A992 Grade 50 which has a tensile strength of 65 ksi.
For Aeos Grades 70 and 80, E90XX and E100XX electrodes should be used, respectively. Based on Clause 5.6 in AWS D1.1-2020, when joining different strengths of steel to each other, the basis for matching electrode strength is with reference to the higher strength steel.
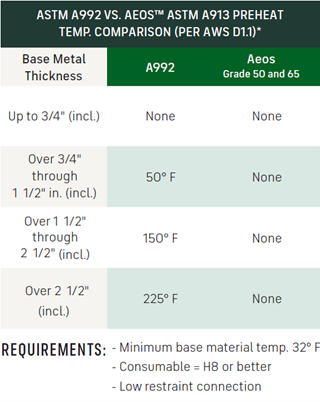
With regard to weld filler material selection, all Aeos sections must use welding consumables with an H8 or better diffusible hydrogen content to achieve the Category D designation.
If Aeos Grade 65 is not selected for a project, specifiers may consider the use of Aeos Grade 50 in place of ASTM A992 or ASTM A572 Grade 50 due to the savings incurred by eliminating preheat.
- For example, when fabricating an element that is 2.5 inches thick, the preheat requirement for A992 steel is 225° Fahrenheit. The preheat requirement for an Aeos Grade 50 or Aeos Grade 65 section with the same thickness is 32° Fahrenheit.
- This differential can lead to significant savings in shop hours, plus energy savings and simplified field welding.
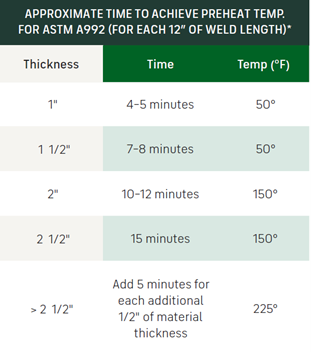
*Note: Labor rates, welder efficiencies, and heating equipment may vary, which can affect these values slightly.
Aeos can be welded to other grades of steel. Referring to Clause 5 in AWS D1.1-2020, different grades of steel from Table 5.3 can be successfully joined by implementing the more stringent preheat and interpass temperature requirements of the grades being welded and the selection of the appropriate filler metal.
For fabricators working with Aeos for the first time, Procedure Qualification Records (PQR) and Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) will need to be developed for welder certifications; however, the welding processes for Aeos and A992 are the same.
Explore Aeos specifications, design tools, case studies and more.
THE AEOS™ WELDING GUIDELINES AT-A-GLANCE
ASTM A913 Properties
- Introduction to the ASTM A913 specification
- Chemistry requirements
- Mechanical properties
- Availability
Welding With Aeos
- Welding procedures
- Filler materials
- Preheat recommendations
- Structural welding design guidance
Fabricating with Aeos
- Tool considerations
- Post rolling treatments
- Testing and inspections
- Welding inspector guidance
Aeos Grade 65 Section Availability
Aeos Case Study: Salesforce® Tower Chicago
Ready to see how Aeos A913 structural steel can benefit your next project? Download the Aeos Welding Guidelines now.
Download the Guide
Download the Aeos™ Welding Guidelines to learn how our domestically produced A913 structural steel can create time, labor and material efficiencies for your next project.
Download Now