Intro to Steel Sheet Piling: Applications and Benefits in Construction

Steel sheet pile is widely used in the construction industry to create permanent or temporary structures to hold back soil or water. Engineers and contractors value the durability, strength and versatility of its uses for multiple applications.
What Is Steel Sheet Piling?
Steel sheet piles are narrow structural sections (sheets) with a vertical interlock that fit together to form a continuous wall in a construction project.
Steel sheet pile comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, including Z-type, flat web and pan type to accommodate varying construction requirements and soil conditions. A sheet pile section's ability to perform depends on its geometry and the soil it is driven into. Walls made from Z sections are corrugated, and the depth of the corrugations and geometry of the shape gives the section the strength and stiffness to resist bending under pressure.
There are two types of steel sheet pile: hot-rolled and cold-formed. While there are differences between these two, the most important distinction is the interlock.
Since hot-rolled steel sheet piling is produced at high temperatures, the interlock tends to be tighter than its cold-formed steel sheet pile counterpart. Typically, looser interlocks are not recommended in extremely hard-driving soil conditions or for walls requiring low permeability. Otherwise, the two types perform similarly.
Types of Steel Sheet Pile:
- Z-Type Sheet Piles (NZ Sheet Pile or PZ Sheet Pile)
Z-shaped sheet piles are called Zs because the single piles are shaped roughly like a horizontally stretched Z, with the interlocks located as far away from the neutral axis as possible to ensure good shear transmission and increase the strength-to-weight ratio. Z piles are the most common type of sheet pile in North America. - Flat Web Sheet Piles
Flat sheet piles work differently from others because they are formed in circles and arcs to create gravity cells held together through the tensile strength of the interlock. The tensile strength and the allowable rotation of the lock are the two main design characteristics. The flat sheet pile cells can be made to huge diameters and heights and can withstand a great deal of pressure. - Pan Type Sheet Piles
The pan-shaped, cold-form sheet piles are much smaller than most other sections and are only intended for short, lightly loaded walls. Pan piles are ideal for installation with smaller equipment in locations with limited space and for low walls where speed is required for construction.
What are the Typical Uses of Steel Piling?
Sheet piling walls are often used in support of excavation (SOE) and form the base of an underground structure such as an underground parking garage. The completed walls are structurally sound and often used for slope and excavation protection to retain a watertight barrier for soil or water to transfer and stabilize pressure from the high side of the wall to the soil in front of it.
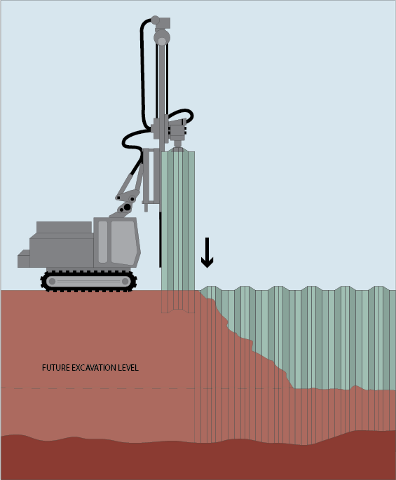
Image source: Geotechnical Engineering
Applications of Steel Sheet Piles:
- Levee Strengthening
- Retaining Walls (temporary and permanent)
- Breakwaters
- Bulkheads
- Environmental Barrier Walls
- Bridge Abutments
- Underground Parking Garages
Options and Approaches for Sheet Piling
Nucor Skyline offers steel sheet piling in ASTM A572 in grades 50 to 65, A588, and A690. A588 and A690 are corrosion-resistant steels used in different environments. These high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels are valued for their strength-to-weight ratio, which provides greater strength in a thinner profile than other steel grades.
Since sheet piling can be utilized for various applications, our strategic approach is changing the economics of conventional below-grade construction. For example, utilizing steel sheet piling as the permanent foundation wall eliminates the need to construct a concrete permanent wall within a shored excavation, which greatly reduces the construction schedule. The reduced schedule equates to significant project savings and a greater return on investment for applicable projects.
What are the Benefits of Sheet Piling?
Versatile and Quick Install Time
Steel sheet piles are applicable for a wide variety of construction and engineering projects for temporary or permanent uses, and they typically take less time to install compared to reinforced concrete retaining walls. Sheet piles are also lighter and require fewer trucks than reinforced concrete.
Strength
The length and design of the pile can be easily adjusted, and the joints are designed to withstand high pressure. After project completion, the structure is strong and durable, thus requiring minimal maintenance depending upon environmental factors surrounding the wall.
Circularity
Steel is infinitely recyclable, and when made using an electric arc furnace (EAF) contributes to a circular process by melting recycled scrap and forming it into new steel. Once a steel pile comes to the end of its use for a temporary project it can be used again, or if it’s at the end of its usable life, it can be recycled as scrap and made into new steel.
Learn More about the Applications of Steel Piling
If you would like to learn more about applications of steel piling, Nucor Skyline offers technical resources and expertise to guide you on upcoming projects.
Visit Nucor Skyline